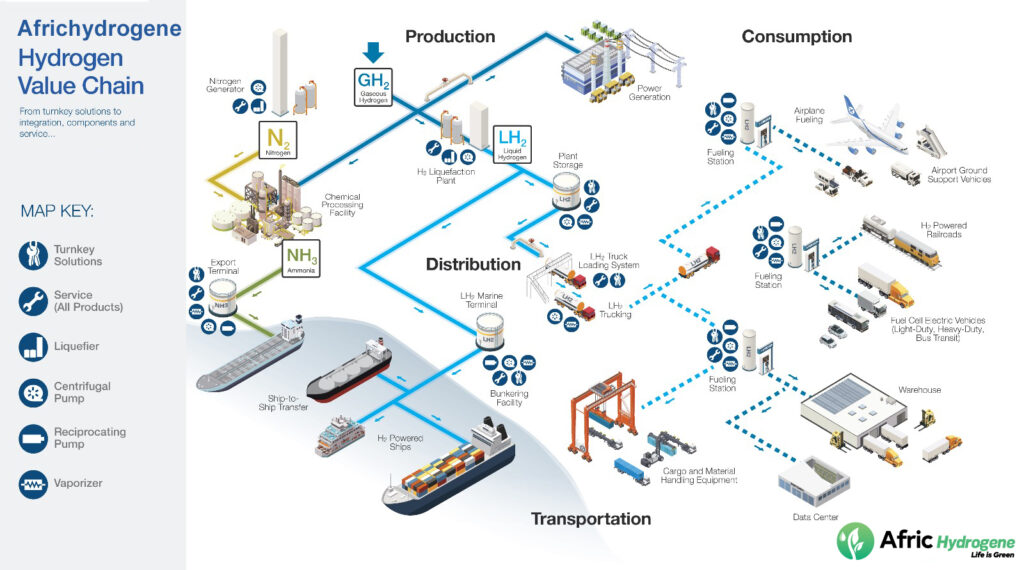
Africhydrogene: Key to Energy Transition and Decarbonization
During the climate summit in the United Arab Emirates, green hydrogen was recognized as crucial for reducing dependence on fossil fuels, with the potential to cut emissions by 25% in refining and ammoniac production by 2050. The market is projected to reach $18.2 billion by 2030. Companies such as BP, Shell, and Indian Oil Corporation are already launching initiatives to integrate green hydrogen, underscoring its importance for achieving climate goals.

Natural Gas Power Plants
Green hydrogen can reduce the carbon footprint of natural gas power plants, making energy production more environmentally friendly. By 2030, it could become more cost-competitive than natural gas.

Green Hydrogen in Heavy Industry
Green hydrogen is essential for decarbonizing heavy industries, which account for about 25% of global carbon emissions, particularly in sectors like steel, glass, and cement production.

Green Hydrogen for Energy Storage and Production
Green hydrogen is effective for long-term energy storage, surpassing batteries in performance. It can also provide backup power through hydrogen fuel cells during extreme weather events. Its conversion to methane via the Sabatier reaction is significant, as methane is a greenhouse gas. According to a September 2023 article, methanation offers a promising alternative to renewable energy and batteries, particularly in sectors such as aviation and maritime transport, where electrification is challenging.

Green Hydrogen as a Transport Fuel
Green hydrogen can transform the transport sector, notably with hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, which numbered 72,193 worldwide by the end of 2022, primarily in South Korea and the United States. It is particularly promising for road freight transport, with companies investing in hydrogen fleets, allowing for quick refueling in ten minutes. Hydrogen is also used in rail and urban transport, with trains, trams, and buses in development. In 2021, there were 6400 hydrogen buses worldwide, 84% of which were in China.

Hydrogen Fuel Cells in Handling and Maritime Transport
Green hydrogen fuel cells are increasingly being used in warehouses, particularly for forklifts. In maritime transport, hydrogen presents a promising solution, with nearly half of zero-emission projects focusing on this technology. Ships can be retrofitted to use hydrogen fuel cells.
Liquid hydrogen is essential for achieving maritime emission reduction targets.
Using green hydrogen for ammonia production is a sustainable alternative to the traditional ammonia production process, which typically relies on natural gas. Ammonia is a key ingredient in fertilizers and other industrial processes, but its production is highly energy-intensive and contributes significantly to CO₂ emissions. By integrating green hydrogen into ammonia synthesis, we can reduce the carbon footprint and move towards a more sustainable process.
Steps for Green Hydrogen-based Ammonia Production:
- Electrolysis to Produce Green Hydrogen:
- Green hydrogen is produced through water electrolysis, powered by renewable energy sources like solar, wind, or hydropower.
- The electrolysis process splits water (H₂O) into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) without producing CO₂, making it a clean source of hydrogen.
2 . Ammonia Synthesis (Haber-Bosch Process):
- The green hydrogen produced is then combined with nitrogen (N₂) from the air to produce ammonia (NH₃) through the Haber-Bosch process.
- The reaction is: N2+3H2→2NH3N_2 + 3H_2 \rightarrow 2NH_3N2+3H2→2NH3
- In traditional ammonia production, this process uses hydrogen derived from natural gas (a process known as steam methane reforming, or SMR), which releases CO₂. By using green hydrogen, the overall process becomes carbon-neutral.
3 . Benefits of Green Hydrogen in Ammonia Production:
- Reduction in CO₂ Emissions: By replacing fossil fuel-based hydrogen with green hydrogen, the ammonia production process emits significantly less CO₂.
- Sustainability: Green hydrogen is renewable, making it a key part of decarbonizing industries that are otherwise hard to electrify.
- Circular Economy: The process produces no waste CO₂, and green hydrogen can be produced locally, enhancing energy security..
4. Global Shift Toward Green Hydrogen:
- Governments and industries are increasingly focusing on green hydrogen as part of their decarbonization strategies. The European Union, for example, has outlined plans for a green hydrogen economy, which includes ammonia production using green hydrogen as a priority area.
Conclusion:
Using green hydrogen for ammonia production is a promising route to reducing the environmental impact of this vital industrial process. With advancements in renewable energy and electrolyzer technology, green hydrogen could play a significant role in making ammonia production more sustainable and less dependent on fossil fuels.
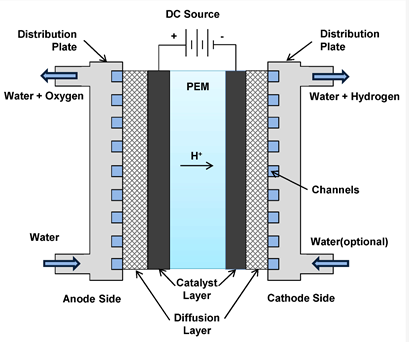
Overall Process The electrolyzer system
is designed to generate hydrogen from tap water using Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolysis which utilizes DC current to electrochemically produce high pressure hydrogen gas. The 5MW hydrogen generation system is a five stack PEM electrolyzer that generates up to 2125 kg/d high purity (99.999%) hydrogen.

Electrolysis
The electrolysis process is the heart of this system.
This 5MW system contains five 1 MW stacks, consisting of 129 electrolysis cells each. Together the five stacks produce max. 2125 kg/d pure, high-pressure hydrogen.
The electrolysis cells are operating on the technical principle of the proton-exchange-membrane (PEM) based water electrolysis concept. In this design ultra pure water is pumped through one side (anode) of the
electrolytic cells, which utilizes direct current to electrochemically produce pure, high-pressure hydrogen gas on the opposite (cathode) side of the cell.
Refer to: Pucture below
Input
* Stack Power Consumption: Up to 5 MW
* Voltage & Frequency:
* 5.4 MW
* Water Consumption:
* 15 liters per kilogram of hydrogen produced
OUTPUT (HYDROGEN GAS)
*Volume: 990 Nm³/h
* Mass : 2,125 kg/day
* Purity : Up to 99.999%
* Pressure : 40 barg / 580 psig (without compressor)
OPERATIONAL FEATURES
- Start-Up Time : 60 seconds for ramp-up
- Average Stack Efficiency : 49.8 kWh per kg of hydrogen
- Load Following Capability :
- Ramp-up : 60 seconds from minimum to maximum load
- Ramp-down : ≤15 seconds from maximum to minimum load
PHYSICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATION
Installed Footprint: Approximately
700 m2
Weight 88 Tons
Productions hours 4500 hrs.
Ambient Temperature Range: -20°C to +40°C (optional wider temperature range available)
Efficiency
The efficienty rate by a load of 100% is 60%
